30
common and how the following correlations (during the pre-processing phase) can be
explained.
A list of all the services can be found in the NSL-KDD can be found in Annex B: table of all the
services in the NSL-KDD dataset. In this section, a brief presentation of the protocols and
services is given, to present a picture of the characteristics of the dataset.
The protocols recorded in the dataset all belong to the transport layer of the OSI model and of
the TCP/IP stack [26], and the network layer (in OSI) or internet layer (in TCP/IP). The transport
layer, which is the most represented in the dataset, is responsible for process-to-process
delivery (by port number addressing), end-to-end connection between hosts, connecting
devices without considering the network fabric, multiplexing and demultiplexing, so that
different applications are simultaneously used over the network, congestion and flow control,
and data integrity/error correction.
In the NSL-KDD, three protocols are found:
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): TCP is the most popular protocol of the transport layer
because it provides reliable transmission of all packages. It does so, by having an
acknowledgment signal for all received packets, and it resends the lost ones. While this is a
great advantage that provides a reliable and safe communication, it adds an additional
overhead due to these features. It is commonly used by protocols such as HTTP and FTP.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol): UDP, unlike TCP, doesn’t provide acknowledgement of the
received packets, thus the connection is not reliable, it relies on a “best effort” approach.
However, it is very simple and comes with much less overhead compared to other protocols.
it is most commonly used in streaming/real time services, such as video or voice streaming.
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol): ICMP is a network/internet layer protocol, despite
sometimes being perceived as a transfer layer one, as the internet layer depends on ICMP for
error and control messages (ping, traceroute, destination unreachable, etc.). It is mainly used
to determine whether or not data has reached its intended destination in a timely manner. In
the case of the NSL-KDD dataset, and TCP data dumps in general, ICMP is usually seen when
the packets are fragmented.
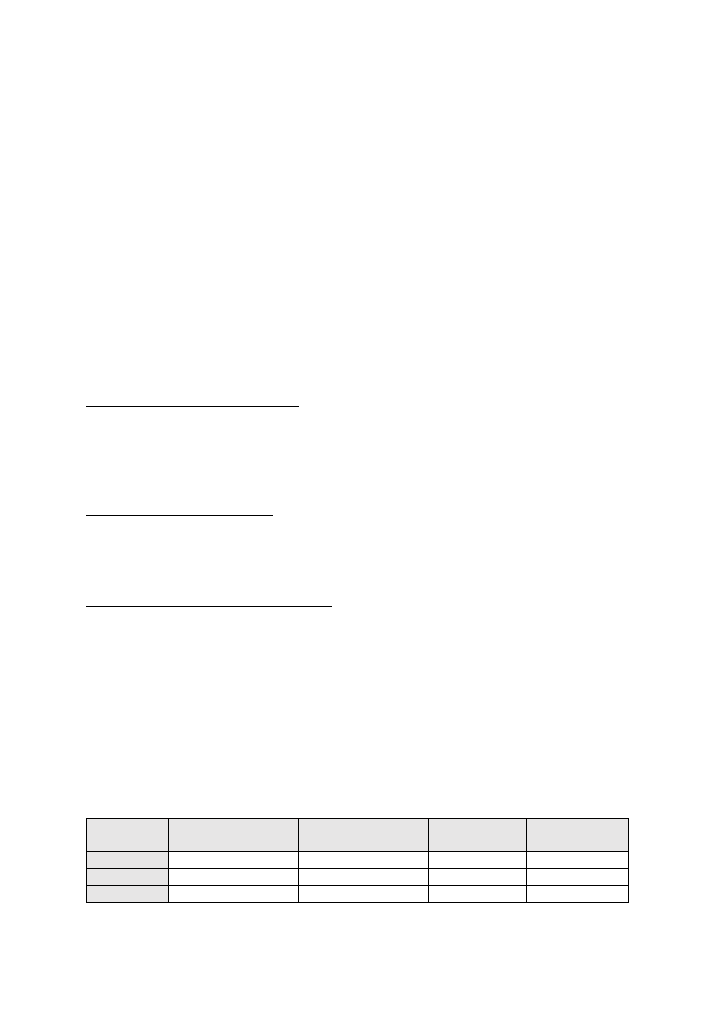
In the NSL-KDD dataset we can find most of the traffic using the TCP protocol, a smaller
percentage using UDP, and a small number of records being ICMP messages, with both the
training and the test sets behaving similarly (Table 3, Figure
13):
Table 3: protocols in the NSL-KDD subsets
Protocol
# in training
set
% in training
set
# in test
set
% in test
set
TCP
102689
81,52%
18880
83,75%
UDP
14993
11,90%
2621
11,62%
ICMP
8291
6,58%
1043
4,63%